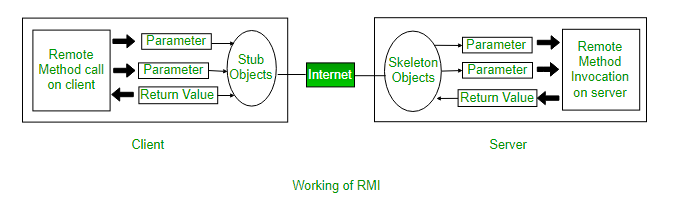
Working of an RMI Application
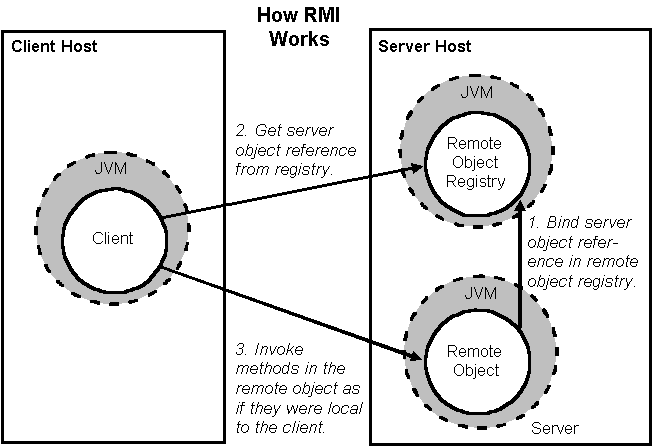
The following points summarize how an RMI application works −
When the client makes a call to the remote object, it is received by the stub which eventually passes this request to the RRL.
When the client-side RRL receives the request, it invokes a method called invoke() of the object remoteRef. It passes the request to the RRL on the server side.
The RRL on the server side passes the request to the Skeleton (proxy on the server) which finally invokes the required object on the server.
The result is passed all the way back to the client.
Working of RMI
The communication between client and server is handled by using two intermediate objects: Stub object (on client side) and Skeleton object (on server side).
Stub Object
The stub object on the client machine builds an information block and sends this information to the server. The block consists of
- An identifier of the remote object to be used
- Method name which is to be invoked
- Parameters to the remote JVM
Skeleton Object
The skeleton object passes the request from the stub object to the remote object. It performs following tasks
- It calls the desired method on the real object present on the server.
- It forwards the parameters received from the stub object to the method.
Steps to implement Interface
- Defining a remote interface
- Implementing the remote interface
- Creating Stub and Skeleton objects from the implementation class using rmic (rmi complier)
- Start the rmiregistry
- Create and execute the server application program
- Create and execute the client application program.
Step 1: Defining the remote interface
The first thing to do is to create an interface which will provide the description of the methods that can be invoked by remote clients. This interface should extend the Remote interface and the method prototype within the interface should throw the RemoteException.
import java.rmi.*;
public interface Search extends Remote
{
public String query(String search) throws RemoteException;
}
Step 2: Implementing the remote interface
The next step is to implement the remote interface. To implement the remote interface, the class should extend to UnicastRemoteObject class of java.rmi package. Also, a default constructor needs to be created to throw the java.rmi.RemoteException from its parent constructor in class.
import java.rmi.*;
import java.rmi.server.*;
public class SearchQuery extends UnicastRemoteObject
implements Search
{
SearchQuery() throws RemoteException
{
super();
}
public String query(String search)
throws RemoteException
{
String result;
if (search.equals("Reflection in Java"))
result = "Found";
else
result = "Not Found";
return result;
}
}
|
Step 3: Creating Stub and Skeleton objects from the implementation class using rmic
The rmic tool is used to invoke the rmi compiler that creates the Stub and Skeleton objects. Its prototype is
rmic classname. For above program the following command need to be executed at the command prompt
rmic SearchQuery
STEP 4: Start the rmiregistry
Start the registry service by issuing the following command at the command prompt start rmiregistry
STEP 5: Create and execute the server application program
The next step is to create the server application program and execute it on a separate command prompt.
- The server program uses createRegistry method of LocateRegistry class to create rmiregistry within the server JVM with the port number passed as argument.
- The rebind method of Naming class is used to bind the remote object to the new name.
import java.rmi.*;
import java.rmi.registry.*;
public class SearchServer
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
Search obj = new SearchQuery();
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1900);
"/geeksforgeeks",obj);
}
catch(Exception ae)
{
System.out.println(ae);
}
}
}
|
Step 6: Create and execute the client application program
The last step is to create the client application program and execute it on a separate command prompt .The lookup method of Naming class is used to get the reference of the Stub object.
import java.rmi.*;
public class ClientRequest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String answer,value="Reflection in Java";
try
{
Search access =
"/geeksforgeeks");
answer = access.query(value);
System.out.println("Article on " + value +
" " + answer+" at GeeksforGeeks");
}
catch(Exception ae)
{
System.out.println(ae);
}
}
}
|
Note: The above client and server program is executed on the same machine so localhost is used. In order to access the remote object from another machine, localhost is to be replaced with the IP address where the remote object is present.
Important Observations:
- RMI is a pure java solution to Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) and is used to create distributed application in java.
- Stub and Skeleton objects are used for communication between client and server side.





